Analyzing water quality discrepancies in Manuhing River and its implications for environmental management
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62090/hn4c8818Keywords:
Manuhing river, pollution indices, river pollution, water qualityAbstract
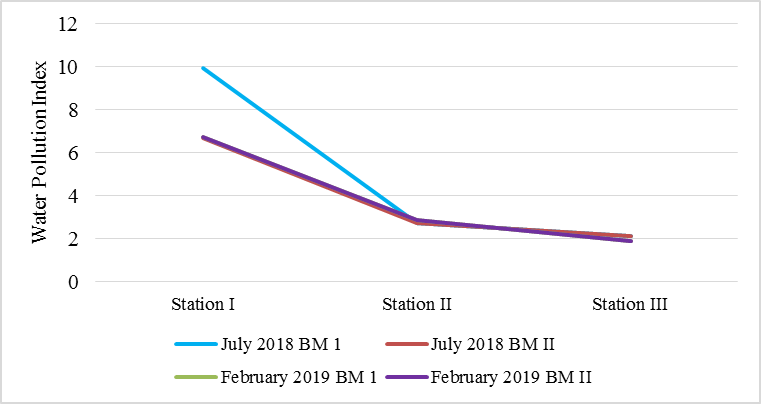
The study focuses on the issue of water pollution in the Manuhing River, which is currently a significant problem in the Gunung Mas District, West Kalimantan, Indonesia. The Manuhing River is located in the upper reaches of the river and is expected to influence the water quality downstream. The research is an observational study, involving direct sampling of water from three designated collection points. Data collection methods include direct observation, documentation, and interviews. The analysis of the data includes the comparison of water quality in the Manuhing River with the established standards, the determination of water quality status based on government regulations, and the management of water quality. The results of the analysis show that the parameters TSS, BOD, Fe, and Total Coliform do not meet the established standards. The water quality status of the Manuhing River falls into the category of heavily polluted to moderately polluted. The results of the one-way ANOVA test between the collection points with pollution indices showed a F-value greater than the F-table, so the null hypothesis (no significant difference) was rejected, indicating that the pollution indices were indeed different in a real sense from each collection point. The efforts that have been implemented so far include monitoring and involving the community, as well as the application of legal sanctions.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ratnayanty, Sulmin Gumiri, Evi Veronika (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









